In my last article, where I tried to give an introduction and basic usage of supervisord process monitoring. There are two more features that someone should know about/be aware of to get the most out of it. Which are:
- interacting with the supervisord web interface and
- using a plugin with supervisord.
So, today, In this small article, I will try to cover these two to make your supervisord experience easier/better. Let’s start with the built-in web interface.
Supervisord Web Interface:
To access the basic web interface, edit the supervisord configuration file(located at /etc/supervisord.conf) in the following section:
[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; (ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface)
;username=user ; (default is no username (open server))
;password=123 ; (default is no password (open server))
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)You have to comment on the first two lines to get it working. After that, run the supervisord in no daemon mode(with -n param), and you should be able to see something like the below in the console log:
2014-07-08 05:25:40,558 CRIT Server 'inet_http_server' running without any HTTP authentication checking
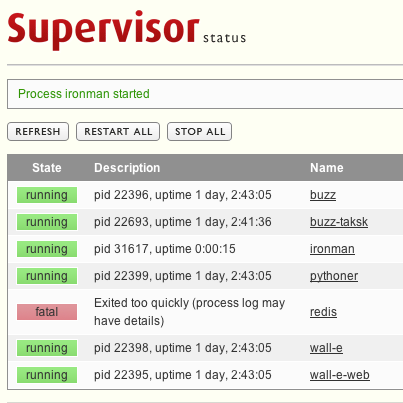
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Which means that it started properly. Now, test the web interface at http://127.0.0.1:9001 URL, which will look something like the below:
As you can see in the screenshot, you can start/stop/restart, see status, log, etc., right from your browser. Pretty cool, isn’t it?
Third-Party SupervisorD Web Interface:
There are some third-party web interfaces available that might be helpful when integrating into a web application. You can find details about them on the supervisord third-party libraries page. Besides easy integration with a web application, some of them also facilitate monitoring more than one server from a single web interface, which is useful in many cases.
Using Plugin:
A plugin can be easily configured via the same configuration file for additional functionality to our existing supervisord installation.
A very useful package is “superlance”. It includes a few very useful plugins for the supervisord. I will show you one example configuration for the ‘memmon’ plugin here. ‘Memmon’ is a plugin that monitors the memory used by the processes and can restart the processes as soon as they go beyond the given boundary size.
After having “superlance” on the system, edit the configuration file below for the “memmon” plugin:
[eventlistener:memmon]
command=memmon -p my-bg-tasks=170MB -m [email protected]
events=TICK_60The above configuration will cause “memmon” to monitor memory usage over 170MB and restart it goes beyond that. It also attaches an event to send a signal every 60 seconds. Now, if the configuration is OK, after starting the supervisord again, with no daemon mode(with -n param), you should see something similar to the following line on the std log:
2014-07-08 05:25:41,564 INFO spawned: 'memmon' with pid 1600Code language: JavaScript (javascript)To test this, try keeping the memory allowance low and feeding your worker process with large data; you should eventually see that the worker restarts with a separate process ID.
Also, to explore further, check out the supervisord plugins page as well.
Final Words:
I hope this article will be helpful to you to some extent. You are most welcome to ask questions, provide feedback, or suggest things via comments. Keep in touch!
Discover more from CodeSamplez.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


Leave a Reply